How Route Optimization Works (Step-by-Step)
Route optimization works by combining your stops and vehicles with real-world
constraints (like time windows, service time, capacity, and working hours),
then computing the best stop order and routes to meet your goals (usually minimizing time or distance).
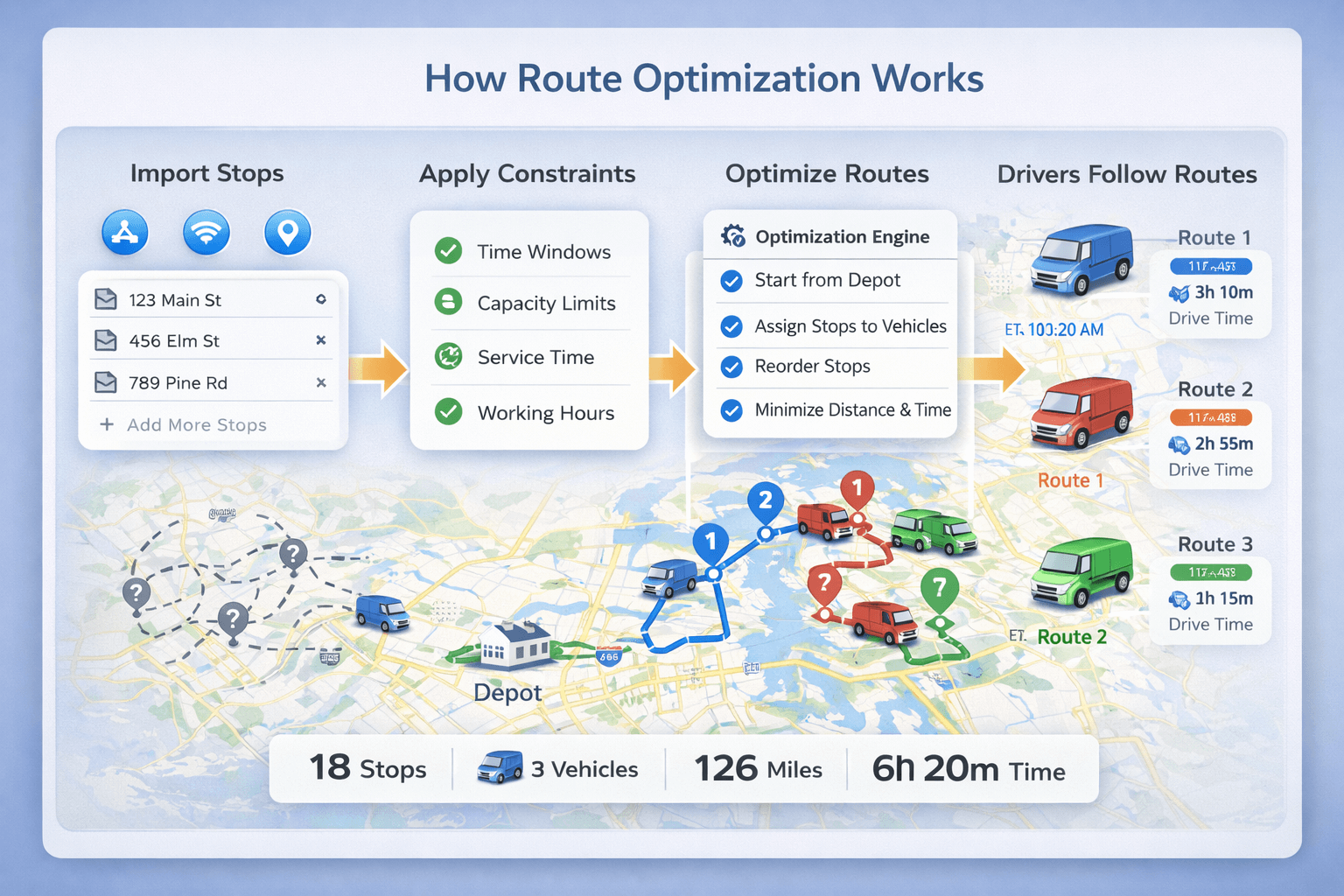 End-to-end route optimization process: inputs (stops and vehicles), constraints, optimization engine, and optimized routes with ETAs.
End-to-end route optimization process: inputs (stops and vehicles), constraints, optimization engine, and optimized routes with ETAs.
If you want the full overview first:
Route Optimization Guide.
Quick overview: what route optimization software does#
Route optimization software solves two core problems:
- Stop sequencing: choose the best order to visit stops.
- Route feasibility: make sure the plan works with real constraints (time windows, hours, capacity).
When multiple vehicles exist, it also solves stop-to-vehicle assignment.
This is why route optimization is often described as a version of the
Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP).
The route optimization process (7 steps)#
This is the most common route optimization workflow used by delivery and field service teams:
- Collect stop data (addresses or coordinates) and optional service time / time windows.
- Add vehicles (start/end location), working hours, and capacity limits.
- Apply constraints like time windows, service time, driver schedules, and capacity.
- Choose an objective (minimize time, minimize distance, balance routes).
- Optimize stop assignment + order (especially for multiple vehicles).
- Generate outputs: routes, ETAs, distance/time totals, reports.
- Dispatch and re-optimize when stops change during the day.
Want the “what is it?” definition first?
What is route optimization?
Constraints: the rules that make routes realistic#
Constraints define what the optimizer is allowed (and not allowed) to do. The most important constraints are:
- Time windows: arrive within allowed ranges (example: 9:00–12:00). Learn more.
- Working hours: vehicles can only operate within shift start/end times.
- Service time: time spent at each stop (delivery, paperwork, installation).
- Capacity: weight/volume limits and per-stop demand.
The more constraints you have, the less effective “manual planning” becomes—and the more value optimization software provides.
How optimization decides the best route#
Route optimization isn’t just “try every possible order.” The number of possible stop sequences grows extremely fast as stops increase.
That’s why optimizers use efficient strategies to produce high-quality routes quickly.
Most systems combine:
- Fast heuristics to generate a good initial plan
- Improvement logic to refine routes while respecting constraints
- Map-based travel times to estimate distance and ETA
If you’re comparing “route planning vs optimization,” see:
Route planning vs route optimization.
How multi-vehicle route optimization works#
Multi-vehicle optimization solves two connected tasks:
- Assign stops to vehicles (who serves which customers)
- Optimize each route (stop order + travel path)
A good multi-vehicle solution balances workload while ensuring routes are feasible inside working hours and time windows.
Learn more:
Route optimization with multiple vehicles.
Outputs: routes, ETAs, and reports#
After optimization, the system typically produces:
- Optimized stop order for each route
- Estimated arrival times (ETAs) per stop
- Total distance and travel time
- Route summaries and reports
- Driver-ready routes for navigation and mobile apps
Want to see why this matters financially?
Route optimization benefits.
Common mistakes that reduce route optimization results#
- Bad addresses or missing coordinates: causes wrong ETAs and detours.
- Ignoring service time: routes look feasible on paper but fail in reality.
- Missing time windows: increases late arrivals and failed deliveries.
- Wrong vehicle working hours: creates overtime and unbalanced routes.
- Too few vehicles configured: forces impossible plans for the volume.
How TrackRoad route optimization works (practical workflow)#
- Add stops manually, paste a list, or import Excel/CSV.
- Add vehicles with start location, working hours, and capacity (optional).
- Add constraints like time windows and service time per stop.
- Optimize to generate routes with ETAs and totals.
- Dispatch to drivers using TrackRoad mobile apps (iOS & Android).
If you want to try the full product:
TrackRoad Route Optimizer.
FAQ#
How does route optimization work?
Route optimization software collects stop and vehicle data, applies constraints like time windows and capacity, then computes the best stop order and routes to minimize time or distance while meeting requirements.
What inputs do I need for route optimization?
You typically need stop addresses or coordinates, optional service times and time windows, and vehicle details such as start location, working hours, and capacity limits.
How does multi-vehicle route optimization work?
Multi-vehicle route optimization assigns stops to different vehicles and optimizes each route while respecting constraints and balancing workload across drivers.
Is route optimization different from Google Maps?
Yes. Google Maps can reorder stops, but route optimization software also supports multiple vehicles, time windows, capacities, working hours, and route balancing.